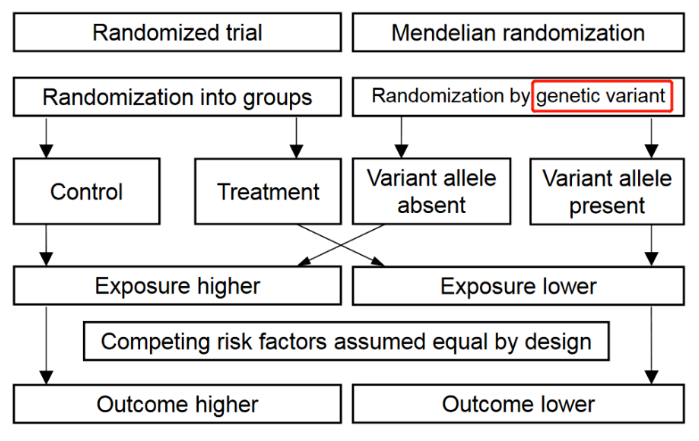
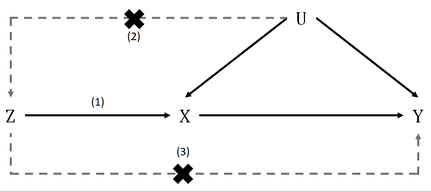
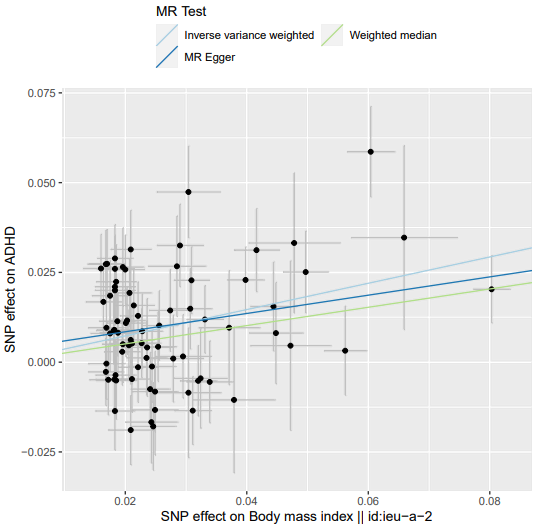
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
| VCF_dat = VariantAnnotation::readVcf('~/upload/GWAS/IEU/ieu-a-2.vcf.gz')
exp_dat = gwasglue::gwasvcf_to_TwoSampleMR(vcf = VCF_dat)
saveRDS(file = 'ieu-a-2.exp_dat', exp_dat)
exp_dat = subset(exp_dat, pval.exposure < 5e-08)
fix_ld_clump_local = function (dat, tempfile, clump_kb, clump_r2, clump_p, bfile, plink_bin) {
shell <- ifelse(Sys.info()["sysname"] == "Windows", "cmd",
"sh")
write.table(data.frame(SNP = dat[["rsid"]], P = dat[["pval"]]),
file = tempfile, row.names = F, col.names = T, quote = F)
fun2 <- paste0(shQuote(plink_bin, type = shell), " --bfile ",
shQuote(bfile, type = shell), " --clump ", shQuote(tempfile,
type = shell), " --clump-p1 ", clump_p, " --clump-r2 ",
clump_r2, " --clump-kb ", clump_kb, " --out ", shQuote(tempfile,
type = shell))
print(fun2)
system(fun2)
res <- read.table(paste(tempfile, ".clumped", sep = ""), header = T)
unlink(paste(tempfile, "*", sep = ""))
y <- subset(dat, !dat[["rsid"]] %in% res[["SNP"]])
if (nrow(y) > 0) {
message("Removing ", length(y[["rsid"]]), " of ", nrow(dat),
" variants due to LD with other variants or absence from LD reference panel")
}
return(subset(dat, dat[["rsid"]] %in% res[["SNP"]]))
}
fuck = fix_ld_clump_local(
dat = dplyr::tibble(rsid=exp_dat$SNP, pval=exp_dat$pval.exposure),
tempfile = file.path(getwd(),'tmp.ld_clump.exp_dat'),
clump_kb = 10000, clump_r2 = 0.001, clump_p = 1,
plink_bin = '/opt/conda/envs/MR/bin/plink',
bfile = "/home/jovyan/upload/GWAS/ld/EUR"
)
exp_dat_clumped = exp_dat[exp_dat$SNP %in% fuck$rsid,]
saveRDS(file = 'ieu-a-2.exp_gwas', exp_dat_clumped)
|